Prion disease treatment has made significant strides, following groundbreaking research that brings hope to patients suffering from these devastating conditions. As scientists explore innovative gene editing therapy, new avenues for combating fatal diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia are opening up. The collaboration among researchers, especially those like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, who bring a deeply personal connection to their work, has fueled advancements in understanding hereditary factors involving the prion protein gene. Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of modifying specific genes to reduce the production of harmful prion proteins, significantly improving the lifespan of laboratory models. This promising research signifies a crucial step toward not only understanding prion diseases better but also developing effective treatments that could ultimately save lives.
Pioneering advancements in the therapy of prion diseases, also known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies, have emerged recently, showcasing the potential to dramatically alter the prognosis for affected individuals. These rare, fatal conditions caused by misfolded proteins include numerous disorders, notably those tied to hereditary mutations in essential genes. Researchers are increasingly turning to novel genetic interventions, such as base editing technology, which seeks to precisely alter genetic material implicated in diseases like fatal familial insomnia. The collaborative efforts of patient-scientists highlight the deep personal investments driving these investigations, enhancing the motivation to find viable therapeutic options. As the scientific community moves closer to initiating human trials, optimism grows for breakthrough treatments that target the underlying causes of prion-related disorders.
Understanding Prion Diseases and Their Impact
Prion diseases are a group of neurodegenerative disorders marked by the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the brain, leading to severe degeneration and ultimately fatal outcomes. These disorders include well-known conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, fatal familial insomnia, and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. The impact of these diseases is profound, not only affecting the individuals diagnosed but also their families who endure the emotional and psychological toll of watching their loved ones deteriorate. Approximately 15% of prion disease cases are inherited, stemming from mutations in the prion protein gene, while the majority occur sporadically without a clear cause. As research continues, understanding the underlying mechanisms of these disorders is paramount for developing effective treatments.
The rarity and complexity of prion diseases pose significant challenges for researchers seeking to find viable treatments. Unlike more common diseases, prion diseases involve a unique pathophysiology, characterized by the infectious nature of misfolded proteins that can induce similar misfolding in healthy proteins. This creates a chain reaction that leads to cellular dysfunction and death. The cognitive and physical decline experienced by patients is not only devastating but is also often accompanied by a prolonged and challenging care process for families. As scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel navigate this intricate landscape, their personal connections to the disease drive their dedication to uncovering therapies that could potentially alter the course of these life-altering conditions.
The Role of Gene Editing Therapy in Treating Prion Diseases
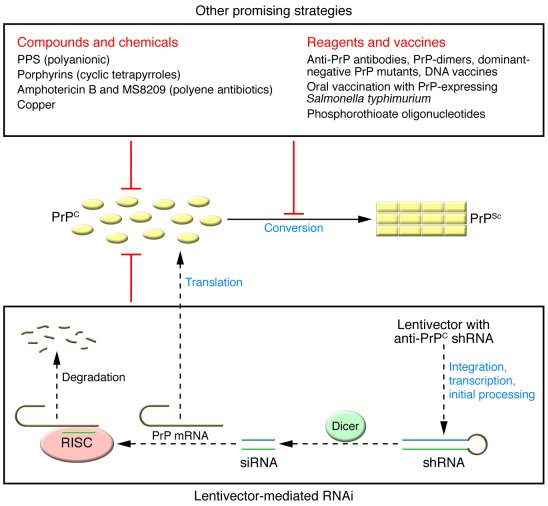
Recent advances in gene editing therapy have opened new avenues for treating prion diseases. By leveraging innovative techniques, such as the base editing method developed at the Broad Institute, researchers are eliminating the harmful effects of mutated prion genes. In studies involving laboratory mice, altering a single nucleotide in the prion protein gene resulted in a significant reduction of toxic protein levels, thus enhancing the lifespans of these mice by over 50%. This breakthrough represents a pivotal milestone in prion disease treatment, demonstrating the potential of gene editing as a powerful therapeutic tool in the fight against these rare disorders. If successfully translated to human trials, this approach might provide a life-changing solution for those afflicted by genetic forms of prion disease.
The application of gene editing therapy addresses the root cause of these diseases by directly modifying the genetic instructions that lead to the production of misfolded proteins. With researchers like David Liu emphasizing caution and rigorous testing before human trials commence, the path forward is laden with necessary checkpoints to ensure safety and efficacy. Additionally, the collaboration among various laboratories illustrates a collective commitment to harnessing the power of genetic research in combating these daunting conditions. The potential of gene editing not only represents hope but also symbolizes a turning point in our understanding of the biological underpinnings of prion diseases, making it a central focus for ongoing research.
Collaborative Efforts in Prion Research
Collaboration in the scientific community plays a crucial role in advancing research for complex diseases like prion disorders. Multi-disciplinary efforts, such as those between neurobiologists, geneticists, and clinicians, enrich the research process through shared expertise and resources. Patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel contribute unique perspectives to the research milieu. Their direct experiences with fatal familial insomnia not only fuel their passion but also ground their research in real-world implications, fostering a sense of urgency and purpose among the research team. Such collaborations enhance resourcefulness and innovation, crucial in tackling the unique challenges posed by prion diseases.
Moreover, the insights garnered from patient experiences provide invaluable feedback to researchers, potentially influencing the design and direction of studies. Researchers like Meirui An highlight the importance of such interactions, as working alongside individuals personally affected by prion disease can inspire novel approaches and heightened commitment to the research goals. This collaborative spirit, combined with cutting-edge scientific techniques, sets a foundation for promising advancements in prion disease treatment that may not have been possible in isolated efforts.
Challenges and Future Directions in Prion Disease Research
Despite the promising breakthroughs in prion disease treatment, significant challenges remain before potential therapies reach clinical trials. Researchers must address concerns such as the complex nature of prion replication and the infectious characteristics of these agents. Furthermore, the delivery mechanisms for gene editing therapies, which currently require multiple viral capsules for effective gene editing, necessitate optimization for increased efficiency and targeting precision. Attention to the safety of these methods is paramount, considering the hazardous implications associated with research on human prion proteins, as highlighted by previous accidents in laboratory settings.
Future paths in prion disease research will likely involve intensified collaboration across various fields, including advanced molecular biology and bioengineering. By enhancing our understanding of prion protein biology and refining gene editing techniques, scientists are poised to overcome the existing hurdles. Researchers are optimistic about the refinement of delivery systems and the identification of safer protocols that will facilitate more effective interventions. Ultimately, these endeavors aim to yield viable treatments for conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia, illuminating a path toward hope for those affected.
The Importance of Patient Advocacy and Involvement
Patient advocacy is a critical aspect of advancing research in prion diseases, as personal narratives contribute to the urgency of scientific inquiry. Individuals like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel bring a unique perspective to the scientific community, having transitioned from patients to researchers. Their commitment to understanding and treating prion diseases has inspired countless others within the medical field to prioritize these rare conditions that might otherwise receive limited attention. Advocacy can also influence funding opportunities and public awareness, essential elements for fostering innovation in a relatively under-researched area.
Moreover, encouraging patient involvement in research helps ensure that the questions being addressed are relevant and impactful for those directly affected by prion diseases. Collaborative efforts between researchers and patients can lead to the development of more meaningful and targeted therapies, ensuring that the scientific goals align with the needs and hopes of the communities involved. As more researchers acknowledge the importance of patient input, the journey toward discovering effective treatments for prion diseases becomes not just a scientific pursuit but a collective mission driven by shared experiences and aspirations.
Funding and Support for Prion Disease Research
Robust funding and support are essential for advancing prion disease research, as the complexities tied to these conditions demand significant resources. Organizations like the National Institutes of Health and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute play a pivotal role in facilitating groundbreaking studies aimed at untangling the mysteries of prion diseases. Grants and funding initiatives allow researchers, including those at the Broad Institute, to explore innovative therapeutic approaches, such as gene editing therapy, which necessitates extensive experimentation and validation.
In addition to governmental support, private institutions and collaborations add crucial backing to research endeavors. Financial contributions from the Prion Alliance, for instance, enhance the capacity for collaborative projects that might struggle for attention in traditional funding landscapes. By pooling resources and expertise from diverse stakeholders, the prion research community can accelerate the pace of discovery, ultimately aiming to develop effective treatments that could change the lives of countless individuals affected by these devastating diseases.
The Future of Prion Disease Therapies: Optimism and Innovation
As research into prion diseases progresses, there is a palpable sense of optimism permeating the scientific community. Innovations in gene editing therapy represent a beacon of hope, offering insight into potentially transformative approaches that could render prion diseases manageable or even effectively treatable. The milestones achieved by researchers reflect not only scientific progress but also a growing belief that solutions are within reach. With techniques like base editing showing promise in laboratory environments, the potential for human applications elicits excitement among both researchers and affected communities.
Collaborative research efforts, robust funding mechanisms, and patient-centered approaches will be integral in driving the development of future prion disease therapies. As researchers continue to refine their methodologies and build on promising findings, the horizon for new treatments appears increasingly bright. The collective goal remains to translate laboratory successes into clinical realities, providing tangible hope for individuals battling prion diseases, and potentially reshaping the landscape of neurodegenerative disorder management.
The Ethical Considerations in Prion Disease Research
Research into prion diseases necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications, particularly given the infectious nature and devastating outcomes associated with these disorders. The potential risks involved in experiments, especially those utilizing human prion proteins, warrant stringent ethical oversight to protect both researchers and the broader community. It is essential that ongoing studies adhere to high ethical standards while balancing the pursuit of knowledge with the responsibility of ensuring that risks are minimized and well-communicated.
Ethics also come into play when involving patient-stakeholders in research processes. While patient involvement enriches the research with crucial perspectives, it raises questions about consent, representation, and the management of sensitive information. Engaging with individuals impacted by prion diseases in a respectful and transparent manner is of utmost importance, fostering trust and collaboration between researchers and the community. Striking a balance between innovative research and ethical responsibility will be pivotal as the field navigates the complexities associated with prion disease investigations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What advancements have been made in prion disease treatment through gene editing therapy?
Recent advancements in prion disease treatment include promising research on gene editing therapy, particularly targeting the prion protein gene. Studies have shown that altering a single base in this gene can significantly reduce misfolded proteins in the brain, as demonstrated in laboratory mice, leading to increased lifespans and providing hope for future treatments.
How does gene editing therapy specifically address conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease?
Gene editing therapy aims to treat prion diseases, including Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, by correcting mutations in the prion protein gene that lead to protein misfolding. This technique has shown potential in reducing harmful protein levels, ultimately offering a pathway toward effective treatments for these fatal conditions.
What is the significance of Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel’s involvement in prion disease research?
Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel are pivotal figures in prion disease treatment research due to their personal connection to fatal familial insomnia, a hereditary prion disease. Their firsthand experience and dedication motivate their efforts to develop effective gene editing therapies, fostering collaboration and innovation in this critical area of study.
What challenges remain before implementing prion disease treatment in humans?
While recent studies on gene editing therapy show promise for prion disease treatment, significant challenges must be overcome. These include optimizing the delivery methods for gene editing tools, ensuring safety, and conducting extensive clinical trials before therapies can be approved for human use.
What role do mouse models play in advancing prion disease treatment research?
Mouse models are essential for prion disease treatment research as they closely mimic human prion diseases, like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Research conducted on these models allows scientists to evaluate the efficacy of gene editing therapies and gain insights into potential outcomes for human patients.
How does the collaboration between researchers impact the development of prion disease treatments?
Collaboration among researchers enhances the development of prion disease treatments by pooling expertise, sharing resources, and fostering innovative approaches. The partnership between scientists like David Liu, Sonia Vallabh, and Eric Minikel exemplifies how diverse skills contribute to breakthroughs in gene editing therapy for prion diseases.
What are the implications of reducing prion protein production in gene editing therapy?
Reducing prion protein production through gene editing therapy could significantly impact the treatment of prion diseases by lowering the levels of toxic proteins in the brain. This reduction has been linked to increased survival in animal studies, indicating that similar approaches may soon lead to therapeutic options for conditions like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Why is human trial readiness crucial for advancing prion disease treatment?
Human trial readiness is a crucial step for advancing prion disease treatment as it ensures that gene editing therapies are tested for safety and efficacy in actual patients. Successful trials will determine the viability of these therapies for conditions like fatal familial insomnia and pave the way for regulatory approval.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Prion Disease Overview | A group of rare and fatal disorders caused by misfolded proteins in the brain. |
| Research Breakthrough | New gene-editing therapy shows promise, reducing harmful proteins by 50% and increasing mouse lifespans by 52%. |
| Personal Motivation | Researchers Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, deeply connected to prion disease, lead their own lab to find a treatment. |
| Collaborative Efforts | The study involves multiple teams from Broad Institute and MIT, using advanced editing techniques developed in David Liu’s lab. |
| Future Steps | While promising, human trials remain years away due to complex safety and efficacy optimizations needed. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment has seen a recent breakthrough with promising research indicating that a gene-editing therapy could significantly reduce harmful protein levels in the brain. This development represents a hopeful pathway towards effective treatments for currently incurable prion diseases. Researchers are now faced with several challenges before human trials can commence, but the personal experiences of the scientists involved lend an extraordinary motivation that drives the research forward. The potential for a practical treatment offers hope to patients and families impacted by these devastating neurodegenerative conditions.