Pregnancy-related deaths have emerged as a pressing public health crisis in the United States, with alarming statistics revealing that over 80% of these fatalities are preventable. Despite being a high-income nation, the U.S. leads the world in maternal mortality rates, which have continued to rise from 2018 to 2022. This trend is exacerbated by significant health disparities, particularly along racial and ethnic lines, with some communities experiencing disproportionately higher rates. Complications such as cardiovascular disease during pregnancy contribute to these tragic outcomes, highlighting the urgent need for improved maternity and postpartum care. Addressing these issues requires concerted efforts to tackle the underlying health disparities that influence maternal health and safety for all women.
The issue of maternal mortality, often referred to as pregnancy-related fatalities, represents a critical challenge in reproductive health. Terms like maternal health inequities and pregnancy complications shed light on the multifaceted nature of this crisis, underpinning the need for comprehensive postpartum support. The increasing incidence of deaths related to cardiovascular disorders during maternity emphasizes the importance of addressing chronic conditions that arise in this vulnerable population. Furthermore, tackling health disparities is essential to ensuring that all women, regardless of race or socioeconomic status, receive the quality care they deserve during and after pregnancy. Understanding these alternative phrases underscores the systemic issues that contribute to high maternal mortality rates and the pressing need for effective healthcare solutions.
Understanding the Rise in Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
The significant rise in pregnancy-related deaths in the United States is an alarming public health issue that raises many concerns. Recent findings indicate that over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable; yet the United States has the highest maternal mortality rates among high-income countries, a figure that continues to escalate. Disparities are evident, with certain groups, namely American Indian and Alaska Native women, facing disproportionately higher mortality rates. These disparities highlight the urgent need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care to protect the lives of expectant mothers.
Research comprehensively shows that socioeconomic factors, racial biases, and lack of access to quality healthcare contribute heavily to these mortality rates. The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated existing vulnerabilities, resulting in a sharp increase in the rate of maternal deaths during 2021. It is crucial for policymakers to understand that improvements in maternal health require systemic changes, focusing on reducing these health disparities to ensure equitable care for all women across various demographics.
The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease on Maternal Mortality
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in recent studies, overtaking previously dominant causes such as hemorrhage. This transition underscores the necessity of addressing chronic health conditions that more women are experiencing during their reproductive years. Many women are entering pregnancy with pre-existing conditions like hypertension, resulting in complications that can jeopardize both maternal and fetal health. Awareness and management of cardiovascular risks should be enhanced within maternal healthcare practices to reduce the toll on expectant mothers.
Furthermore, understanding the evolution of cardiovascular issues during pregnancy calls for increased vigilance from healthcare providers. With the alarming statistic that a significant number of pregnancy-related deaths occur in middle-aged women, it emphasizes the need for early interventions and continuous monitoring throughout pregnancy. Such measures can help mitigate risks associated with cardiovascular diseases, fostering a safer environment for both mothers and their children.
The Importance of Postpartum Care in Reducing Maternal Mortality
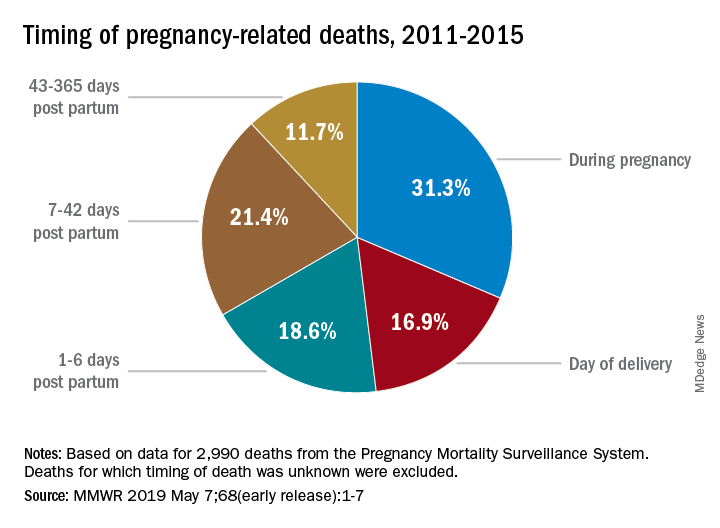
Postpartum care is a critical aspect of maternal health that often receives insufficient attention. Recent data has revealed that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur in the late postpartum phase, prompting calls for a reevaluation of the postpartum care framework in the U.S. Traditional healthcare paradigms typically define maternity care as a six-week affair post-delivery, but this limited perspective fails to capture the continuum of care needed to support new mothers. This oversight can lead to missed opportunities for intervention in cases where complications arise following childbirth.
Expanding the definition of postpartum care to include a longer recovery period is essential for improving maternal outcomes. This could involve regular follow-ups and support services to monitor mothers’ health, especially those with high-risk profiles. Investing in comprehensive postpartum care would not only help in significantly reducing pregnancy-related deaths but also address lingering health issues that new mothers may face long after childbirth.
Addressing Health Disparities in Maternal Care
Health disparities are a prominent issue in maternal care, contributing to significantly higher pregnancy-related mortality rates among certain racial and ethnic groups. The study highlights stark differences, with American Indian and Alaska Native women exhibiting rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Such disparities raise critical questions about the accessibility and quality of maternal healthcare services across different demographics. Tackling these inequities is imperative for enhancing overall maternal health outcomes.
To effectively address health disparities, initiatives must focus on creating a more equitable healthcare infrastructure. This involves increasing access to quality prenatal and postpartum care for all women, ensuring that those in underserved populations receive the necessary support. Additionally, policies must be implemented at state and federal levels to eliminate systemic biases that have historically marginalized certain groups, thereby fostering a more inclusive approach to maternal health.
The Need for Improved Tracking of Maternal Health Outcomes
Accurate tracking of maternal deaths is crucial to understanding trends and determining the effectiveness of health interventions. Prior to 2018, the U.S. lacked a consistent national system for tracking pregnancy-related mortality, which hampered efforts to identify patterns and address the issue effectively. The introduction of a pregnancy checkbox on death certificates has improved data collection, but widespread implementation across states remains inconsistent. Enhanced tracking could provide invaluable insights into maternal mortality, ultimately equipping healthcare providers and policymakers with the information needed to enact meaningful changes.
By refining the methodologies used to capture maternal health data, the healthcare system can better analyze the causes of pregnancy-related deaths. This information is essential for developing targeted strategies that address specific health issues, thereby reducing overall maternal mortality rates. Further investment in public health infrastructure to sustain this data reporting system is critical, as it will enable ongoing evaluation and improvement of maternal care across the nation.
Recommendations for Postpartum Care Improvements
In light of the rising maternal mortality rates, recommendations for improving postpartum care are more critical than ever. Many health experts advocate for extending the postpartum period recognized by healthcare systems to better encompass the ongoing needs of mothers after childbirth. By addressing postpartum issues beyond the traditional six-week window, healthcare providers can create more robust health plans that continue to support mothers in managing complications such as cardiovascular disease or mental health challenges.
The incorporation of holistic postpartum programs that include counseling, physical checkups, and lifestyle support can make a significant difference. For instance, women should have access to nutritional guidance, mental health resources, and chronic disease management strategies during the year following childbirth. This comprehensive approach not only aids recovery but also ensures that mothers remain healthy and vital, ultimately leading to better outcomes for themselves and their children.
The Role of Policy in Maternal Health Outcomes
Policies play an instrumental role in shaping maternal health outcomes. Variations in state policies regarding maternal care significantly contribute to the disparate pregnancy-related mortality rates seen across the country. States like California, which have implemented innovative maternal health initiatives, demonstrate that effective policy interventions can lead to positive health outcomes. Policymakers should examine these successful models and explore how similar strategies can be adopted in states with poorer maternal health statistics.
Moreover, advocacy for enhanced funding and resources dedicated to maternal health is crucial. With alarming cuts to public health infrastructure, there is an urgent need to prioritize maternal care, especially in underfunded areas. Policymakers must recognize that addressing maternal health holistically, including prenatal, labor, delivery, and postpartum care, is essential for reversing these disturbing trends in maternal mortality and ensuring that every woman has access to safe and effective healthcare.
Innovative Solutions for Maternity Care Today
Integrating innovative solutions into maternity care has the potential to significantly enhance maternal health outcomes. Technological advancements, such as telehealth services, have emerged as vital resources, particularly in regions with limited access to healthcare facilities. These platforms allow for continuous care management, enabling healthcare providers to monitor the health of pregnant women and address potential complications proactively. By utilizing modern technology, healthcare systems can bridge gaps in care and provide necessary support to all mothers.
In addition to tech-based solutions, community-driven approaches can foster stronger support networks for expecting and new mothers. Programs that focus on peer support, maternal education, and community health workers can empower women and enhance their overall health literacy. These initiatives promote a culture of care and connection, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and a reduction in pregnancy-related complications.
The Importance of Continuous Health Education for Pregnant Women
Continuous health education for pregnant women is vital for addressing both immediate and long-term health challenges. As many expectant mothers navigate complex health pathways, ongoing education can empower them to make informed decisions about their health and their baby’s wellbeing. This education should encompass all aspects of pregnancy health, including managing pre-existing conditions, recognizing warning signs of complications, and understanding the importance of follow-up care during and after pregnancy.
Healthcare providers must prioritize the dissemination of clear and accessible health information tailored to the diverse needs of pregnant women. Workshops, resources, and support groups that address specific issues—such as managing hypertension or understanding postpartum recovery—can considerably enhance mothers’ confidence in handling their health. Ultimately, prioritizing education is an essential step towards reducing pregnancy-related deaths and improving maternal health overall.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The most significant cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. is cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of these fatalities. Other leading causes include hemorrhage and complications such as hypertension and stroke. Understanding the prevalence of these conditions is crucial in addressing maternal mortality rates effectively.
How do health disparities contribute to pregnancy-related deaths?
Health disparities play a vital role in the prevalence of pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. American Indian and Alaska Native women, for instance, face significantly higher mortality rates compared to white women, highlighting the need for equitable healthcare access and tailored maternal care to reduce these disparities.
What role does postpartum care play in reducing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is essential in reducing pregnancy-related deaths, as nearly a third of these fatalities occur between 42 days and one year after childbirth. Effective follow-up care and support during this period can address complications arising after delivery, ultimately leading to better maternal health outcomes.
How does the U.S. maternal mortality rate compare to other high-income countries?
The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, largely due to systemic issues in healthcare access and quality. A study revealed that many of the pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, indicating a critical need for improved prenatal care and post-delivery support.
What innovative solutions are being proposed to decrease pregnancy-related deaths?
Proposals to reduce pregnancy-related deaths include enhanced public health investment, equitable healthcare policy reforms, and innovative care solutions aimed at improving the quality of maternal health services during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Tailoring these solutions to address the specific needs of different states can also facilitate better outcomes.
Why is it important to include late maternal deaths in discussions about pregnancy-related mortality?
Including late maternal deaths—those occurring from 42 days to one year after childbirth—in the discussion of pregnancy-related mortality is vital because it provides a more comprehensive overview of maternal health challenges. This recognition can lead to improved healthcare systems that offer continued support and monitoring beyond the immediate postpartum period.
What are the implications of rising pregnancy-related deaths among younger populations?
The rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths among younger populations, particularly those aged 25 to 39, indicate an increasing prevalence of chronic health conditions like hypertension at a younger age. This trend necessitates a reevaluation of how pregnancy-related risks are managed in this demographic to enhance maternal health outcomes.
What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on pregnancy-related deaths?
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated existing health crises and is believed to have contributed to the sharp increase in pregnancy-related deaths observed in 2021. The pandemic’s impacts on healthcare access and the management of chronic conditions have highlighted the urgent need for reforms in maternal health protocols.
What steps are being taken to improve the tracking of pregnancy-related deaths?
Efforts to improve the tracking of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include the implementation of a standardized pregnancy checkbox on death certificates, which allows for consistent data collection. This initiative, in effect since 2018, aims to enhance the understanding and visibility of maternal mortality trends for better policy and public health responses.
How can we better address the systemic issues contributing to pregnancy-related deaths?
Addressing systemic issues contributing to pregnancy-related deaths requires a multifaceted approach, including investing in public health infrastructure, implementing equitable healthcare policies, and fostering community-based solutions that recognize and mitigate the diverse needs of pregnant individuals across different states.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Preventability of Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are considered preventable. |
| Maternal Mortality Comparison | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. |
| Recent Trends | From 2018 to 2022, maternal mortality rates increased, peaking in 2021 likely due to COVID-19. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest mortality rates, nearly four times higher than white women. |
| Leading Causes | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause, accounting for over 20% of deaths. |
| Importance of Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year postpartum. |
| Policy Recommendations | Increase investment in public health and address state-level care quality disparities. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths have been on the rise in the United States, particularly from 2018 to 2022, reflecting significant disparities influenced by state, race, and ethnicity. The study underscores the crucial need for improved prenatal care and robust postpartum support systems to tackle this alarming trend. As evidenced by research from the National Institutes of Health, notable preventative measures can be implemented to significantly reduce mortality rates across demographics, emphasizing the urgency for systemic health care reforms.