Is sugar addictive? This question sparks ongoing debate among nutritionists and health enthusiasts alike, prompting many to ponder whether their cravings for sugary treats are akin to substance dependency. While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards, its impact on our brain chemistry can lead to consistent sugar cravings and an insatiable desire for processed foods. As we indulge in these ultra-processed products, we may unknowingly invite a cycle of overconsumption, increasing our exposure to the health risks of sugar. Understanding the true nature of sugar addiction requires us to explore the fine line between craving and addiction, and how our diets define our relationships with sweetness.
When considering the topic of sugar and its potential addictive qualities, it’s essential to explore related concepts such as sweet cravings and the psychological dependence on certain foods. Many individuals find themselves falling into patterns of consuming highly palatable and processed snacks, which can trigger almost compulsive behavior similar to that seen with traditional addictive substances. The lure of these sugary delights often leads to repeated overindulgence, raising concerns about the long-term health impacts associated with excessive sweet intake. By examining the dynamics of this dependence, we can gain insights into our dietary habits and the broader implications of sugar in our lives.
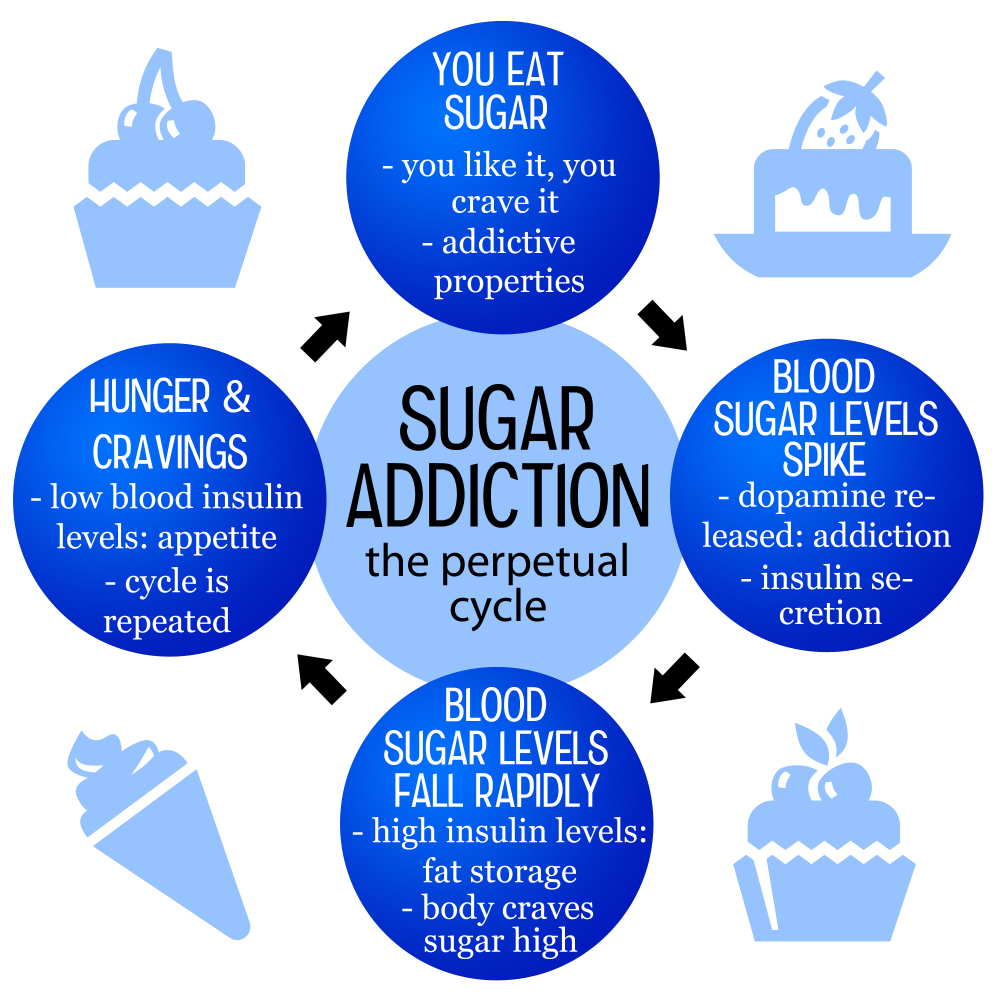
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a term that often sparks considerable debate among nutritionists and health professionals. While substances like alcohol, nicotine, and opiates are readily classified as addictive due to their severe physiological and psychological withdrawal symptoms, sugar does not fit neatly into this category. Research indicates that sugar can provoke cravings similar to those induced by addictive substances, leading to compulsive eating behaviors. However, it is essential to recognize that while sugar may share some addictive qualities, especially in the context of processed foods, it is not officially deemed an addictive substance according to current clinical standards.
Understanding why sugar can feel addictive lies in its ubiquity in our modern diets, particularly through ultra-processed foods that are engineered to be highly palatable. These products often combine added sugars with unhealthy fats and sodium, increasing cravings in consumers. When individuals attempt to cut sugar out of their diets abruptly, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as anxiety, headaches, or dizziness, akin to those related to more traditionally recognized addictions. Therefore, while sugar does foster a dependence-like relationship in many, it’s crucial to understand the context and relevance of these cravings.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Cravings
Processed foods have become a staple in many diets, often loaded with excessive amounts of added sugars. These foods are designed to be addictive — with combinations of sugar, fat, and salt that tantalize our taste buds and spur on cravings. The convenience and accessibility of these products mean that many people turn to them for comfort or a quick energy boost, perpetuating a cycle of habitual consumption. As a result, the sugar-laden snacks and drinks become hard to resist, which raises the question of how deeply these cravings are rooted in our psyche and physiology.
Moreover, the consumption of these processed options contributes significantly to the daily sugar intake of an average American, nearing 20 teaspoons a day, which exceeds recommendations set by health authorities. This excess can lead to adverse health consequences, including obesity and diabetes, underscoring the critical nature of addressing sugar consumption in the context of processed foods. Encouraging consumers to read food labels and be mindful of their sugar intake is a vital step in combating sugar cravings and the health risks associated with high sugar consumption.
Health Risks Associated with High Sugar Consumption
High sugar consumption is linked to various health risks that extend beyond simple weight gain. Studies have shown that excessive sugar intake can lead to chronic health issues, including heart diseases, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. The American Heart Association recommends significantly lower consumption of added sugars than the average person currently ingests, which highlights the health crisis posed by sugar-laden foods. Individuals often underestimate the health risks associated with sugar, as they are more attuned to the dangers of more classically recognized addictive substances like alcohol and tobacco.
The insidious nature of sugar addiction and the health risks it carries cannot be overstated. While sugar plays an essential role in our diet, primarily sourced from fruits and whole grains, it’s the added sugars present in processed snacks and drinks that pose a much greater threat. Public health initiatives focusing on reducing sugar intake are critical, which involves educating consumers on the impact of sugar on their overall well-being and advocating for healthier eating habits, integrating a careful balance of sweetness without the adverse health effects.
Why Moderation is Key in Sugar Consumption
Moderation in sugar consumption is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. While it’s unrealistic to eliminate sugar entirely, especially since it naturally occurs in many nutritious foods, controlling the amount of added sugars consumed is vital. Reducing intake gradually is often more effective than abrupt cessation, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms that discourage lasting dietary changes. By slowly diminishing added sugars in your diet, individuals can adjust their palates and reduce cravings without feeling deprived.
Learning to enjoy food in moderation allows people to indulge in sweetness without compromising their health. It’s essential to recognize that when consumed in low to moderate amounts, sugar can enhance flavors and contribute positively to our diet. The focus should be on making informed choices about the types of sugars consumed, prioritizing naturally occurring sugars found in whole foods over added sugars in processed goods. Establishing a balanced approach to sugar can lead to healthier eating patterns and overall well-being.
The Psychological Aspect of Sugar Cravings
The psychological aspects of sugar cravings are complex and multifaceted. Sugar can activate the brain’s reward system, similar to how addictive substances trigger pleasurable sensations, leading to a strong desire for continued consumption. This mechanism can create a feedback loop where individuals seek out sugary foods for comfort or immediate gratification, especially during times of stress or emotional distress. Understanding this psychological component is crucial for anyone looking to break free from the grips of sugar addiction.
Additionally, emotional eating often contributes to sugar cravings, where individuals use food as a coping mechanism or emotional support. Recognizing triggers that lead to sugar cravings can be a transformative step toward healthier habits. Individuals may benefit from mindfulness techniques or behavioral strategies that help reshape their relationship with food beyond merely seeking immediate rewards, fostering resilience against the allure of high-sugar processed foods.
Building a Healthy Relationship with Sugar
Establishing a healthy relationship with sugar involves understanding its place in your diet without letting it dominate your choices. By acknowledging the role of sugar in providing enjoyment and satisfaction in foods, individuals can learn to appreciate it in moderation. The focus should shift from viewing sugar as an enemy to understanding it as a component that can be part of a balanced diet when consumed wisely. The key is moderation and mindfulness.
Furthermore, integrating more whole foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help diminish dependence on added sugars found in processed foods. These foods are not only more satisfying but also come with additional amino acids, fiber, and nutrients that support overall health. A thoughtful approach to eating can help reduce strong cravings for added sugars, leading to a more balanced and fulfilling dietary experience.
The Importance of Label Reading
Label reading has become increasingly vital in the fight against excessive sugar consumption. With many foods being deceptively marketed as healthy, understanding nutritional labels helps consumers identify added sugars lurking in everyday products. By examining ingredients carefully, individuals can make informed choices, avoiding misleading claims that imply low sugar content while still containing high amounts of sweeteners.
Additionally, awareness of how sugar is classified on labels — under various names such as sucrose, high fructose corn syrup, and agave nectar — allows consumers to recognize their true sugar intake more effectively. This practice can aid in reducing overall consumption, encouraging individuals to choose products that align better with their health goals and fostering a more conscious approach to their dietary habits.
Reducing Sugar Intake Gradually
Taking gradual steps to reduce sugar intake is generally more sustainable than attempting to eliminate it all at once. Abruptly cutting out sugar can lead to withdrawal symptoms that are discouraging for many and can result in a cycle of temptation and guilt when cravings become overwhelming. Instead, slowly cutting back on added sugars, such as those found in sweetened beverages and treats, allows the body to adjust to lower sugar levels smoothly.
Incorporating small changes, such as choosing unsweetened options or substituting with healthier alternatives, can significantly reduce cravings over time. Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet with wholesome foods can help stabilize energy levels and foster better eating habits, ultimately leading to a healthier relationship with sugar and reduced cravings for processed foods.
Finding Alternatives to Satisfy Sweet Tooth
Exploring alternatives to traditional sugary snacks can be an effective strategy in managing cravings while still enjoying sweet flavors. Options such as fruit, yogurt with natural sweeteners, or homemade treats using honey or maple syrup can satisfy one’s sweet tooth without the pitfalls associated with excess refined sugar. Incorporating these alternatives into your diet encourages a more health-conscious approach to sweetness.
Furthermore, experimenting with spices like cinnamon or vanilla can add sweetness to foods without the need for added sugars. These natural enhancements not only flavor foods but can also provide additional health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory properties. By broadening one’s palate and seeking out healthier substitutes, it’s possible to enjoy sweetness in a way that supports overall well-being, reducing reliance on processed foods and mitigating sugar cravings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol and nicotine?
Sugar does increase cravings and can lead to compulsive eating behaviors; however, it is not classified as an addictive substance in the same way as alcohol or nicotine. While sugar can create dependency-like symptoms, particularly with ultra-processed foods high in added sugar, it does not evoke the same severe withdrawal symptoms as these substances.
What are the signs of sugar addiction?
Signs of sugar addiction include intense cravings for sugary foods, withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety after reducing sugar intake, and habitual consumption of processed foods high in sugar. Recognizing these symptoms can help individuals manage their sugar cravings effectively.
How does sugar addiction affect health?
Sugar addiction can contribute to numerous health risks, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. High consumption of added sugars, especially from processed foods, can lead to increased caloric intake and poor nutrition, which negatively impacts overall health.
Can I eliminate sugar cravings without going cold turkey?
Yes, it is advisable to gradually reduce sugar intake instead of eliminating it abruptly. Going cold turkey can lead to withdrawal symptoms, making it more challenging to break the cycle of sugar cravings. Slowly decreasing added sugars can help manage cravings effectively.
What role do processed foods play in sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, which enhances their palatability and increases cravings. These foods can lead to habitual consumption and create a cycle of dependence, making it harder for individuals to resist sugar-laden snacks and meals.
Is it safe to consume sugar in moderation?
Yes, consuming sugar in moderation is generally safe and can even enhance the flavor and enjoyment of foods. The key is to limit added sugars to recommended amounts—no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women per day, as advised by the American Heart Association.
How can I manage sugar cravings effectively?
To manage sugar cravings effectively, focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Staying hydrated, getting enough sleep, and practicing mindful eating can also help reduce cravings and support healthier choices.
What is the difference between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars?
Naturally occurring sugars are found in foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy, which provide essential nutrients and fiber. Added sugars, on the other hand, are included in processed foods and beverages and offer little nutritional benefit. It’s important to distinguish between the two when considering sugar addiction.
| Key Point |
|---|
| Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, based on current clinical criteria. |
| Sugar can create cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, similar to addictive substances, but effects are less severe. |
| Ultra-processed foods containing sugar lead to habitual consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms when eliminated. |
| Moderation is important; low to moderate sugar intake does not have major health consequences. |
| American Heart Association recommends limits on added sugar: 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, much less for children. |
| Gradually reducing sugar intake is advised instead of abrupt elimination to avoid negative effects. |
| Sugar can enhance flavor and pleasure in the diet, indicating a need for moderation rather than complete avoidance. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutrition experts. While sugar does produce cravings and compulsive eating tendencies similar to addictive substances, it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction. The consumption of ultra-processed foods high in sugar is a significant factor in these cravings, but the negative consequences can often be managed with moderation. Awareness of sugar intake and reducing added sugar gradually can lead to healthier eating habits, emphasizing that while sugar has some addictive qualities, it is essential to distinguish it from substances like alcohol and nicotine.